© 2024 Emergent Health Partners, All Rights Reserved

Our results speak for themselves. See our paramedic program student outcomes here.
The HVA Center for EMS Education paramedic training program is a 14-month course totaling 1,200 classwork, lab, clinical, and internship hours. This course prepares students to take the National Registry paramedic exam, obtain paramedic licensure, and work as competent paramedics in the field.
Our program is approved by the MDHHS Division of EMS and Trauma and is accredited by the Committee on Accreditation of Educational Programs for the Emergency Medical Services Professions (CoAEMSP).
The goal of the Center for EMS Education is to prepare Paramedics who are competent in the cognitive (knowledge), psychomotor (skills), and affective (behavior) learning domains to enter the profession.
Course model: This asynchronous program has virtual lecture options, independent online coursework, and in-person labs.
The first day of class is a mandatory in-person day. All students must report to Ann Arbor for the first day of class.
January 6, 2025 – February 11, 2026
Virtual lectures, independent online coursework, and in-person labs.
Registration: November 20 – December 20, 2024, or until the course reaches capacity.
Occasionally, Saturday lab dates may be required and will be announced after the start of class.
Students may choose to complete their labs at our Ann Arbor or Jackson locations.

Jackson Location
Jackson College
2111 Emmons Rd. Jackson, MI 49201
Ann Arbor Location
Huron Valley Ambulance
1200 State Cir. Ann Arbor, MI 48108
Tuition: $8,499
+ an additional cost for uniforms, textbooks, supplies, drug screen, and background check. (around $1,100)
Note
Tuition is broken into three payments of $2,833.
To be considered for acceptance into the HVA EMS Education paramedic program, prospective students must:
During this 14-month course, students will learn the required skills to successfully obtain a paramedic license and serve as a paramedic.
Students will obtain the following required certifications:
Our course curriculum covers:
+ Coursework: Students will complete weekly online coursework. Students are required to stay up-to-date on assigned work and the course schedule.
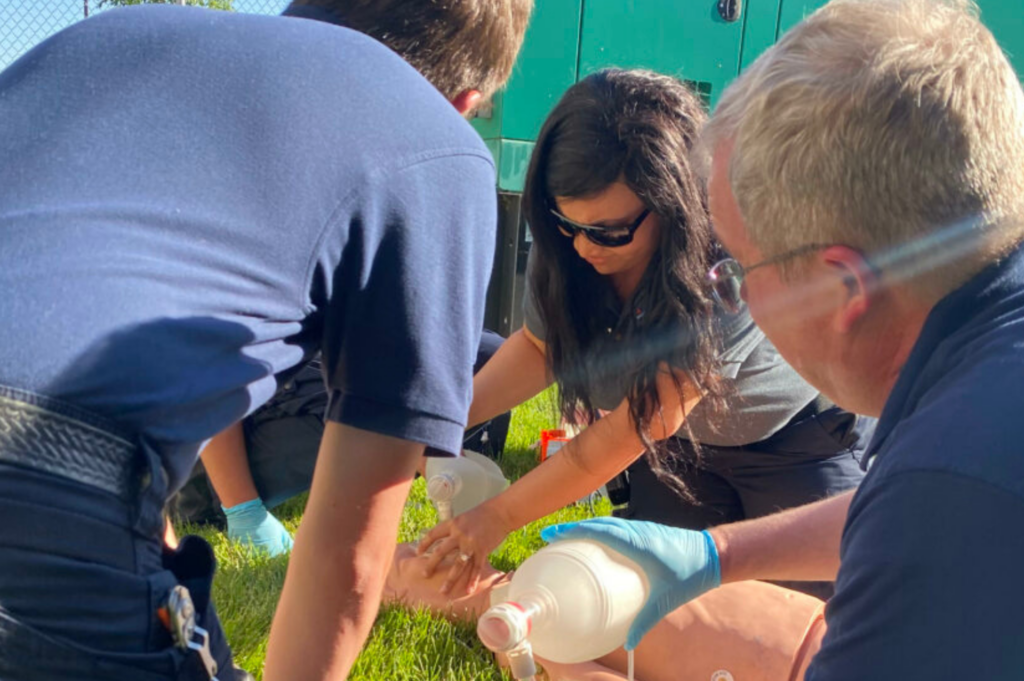
+ Labs: The labs are hands-on learning experiences completed with modern equipment used on ALS and BLS ambulances.
Labs are held at our Ann Arbor or Jackson locations.
Students in both lab locations are trained with modern prehospital equipment. HVA Paramedic Instructor Coordinators run the labs at both locations.
Ann Arbor:
Jackson:
+ Clincials:
Clinicals will be scheduled after the start of class. Students are required to complete:
+Internship:
The final six weeks of the program are your Capstone Internship. During this time, students gain the skills and confidence needed to serve as an entry-level paramedic.
The capstone entails:
A paramedic is a licensed, highly trained first responder and medical provider.
Paramedics respond to 911 calls in an ambulance and provide advanced out-of-hospital emergency care and life-saving interventions to sick and hurt individuals. Paramedics also transport patients by ambulance from the scene of an emergency to a healthcare facility.
Paramedics work under protocols approved by a physician, make patient-care decisions, and supervise team members with lower levels of licensure during calls.
A paramedic license allows the provider a greater scope of practice than an EMT.
Some examples of skills paramedics perform are:
If you answer yes to most of these questions, advancing your career in EMS to paramedic could be the perfect fit:
An EMT license is needed to begin a career in EMS. EMTs are licensed to perform Basic Life Support and non-invasive stabilizing treatments and procedures. An EMT is also known as an EMT Basic or an EMT-B.
A paramedic license is more advanced than an EMT license. Paramedics are trained to perform Advanced Life Support measures, which include medication administration and invasive procedures. To become a paramedic, you must first earn an EMT license. A paramedic is also known as an EMT-Paramedic or EMT-P.
Paramedics can continue to advance their skills and obtain additional certifications. Paramedics can train for:
Paramedics can work for private or government ambulance services, fire departments, or as techs in Emergency Departments.
Positions for paramedics are also available at national parks, with some resorts or cruise ships, and other remote or outdoor areas where immediate medical care may be needed.
Registration for the Winter 2025 course opens on November 20!
Phone: 734-477-6331
Administrative office hours: 8:00 am – 4:30 pm, Monday – Friday
Get updates about future classes and enrollment dates.
© 2024 Emergent Health Partners, All Rights Reserved